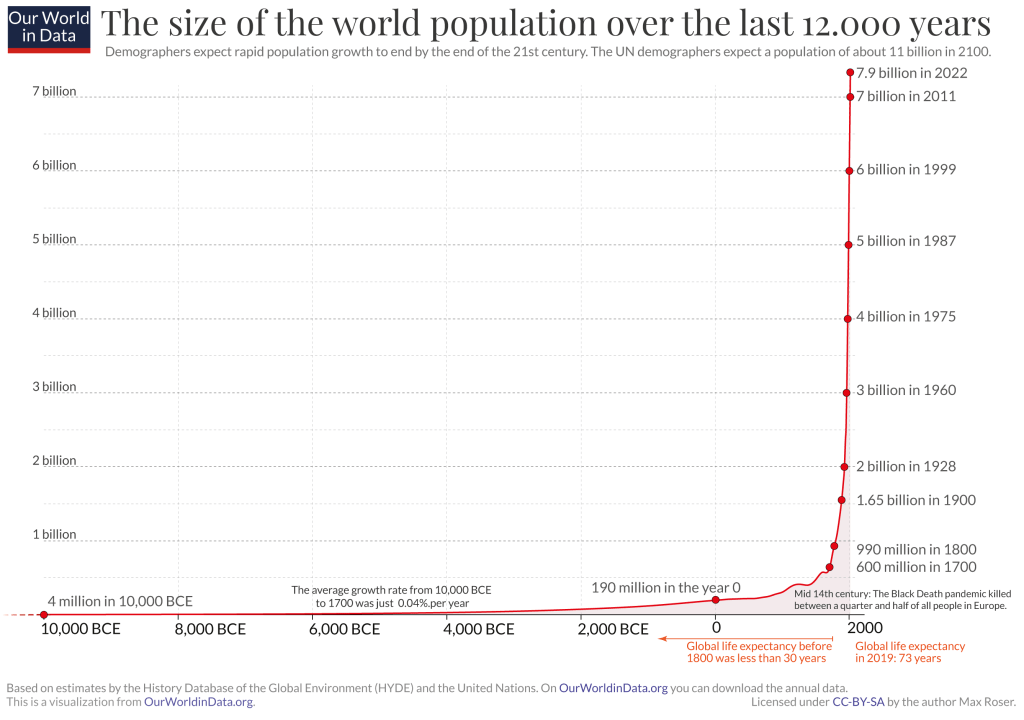
If you didn’t know, China has had negative population growth for the past 4 years. Japan has had negative population growth for the past 15 years. The public and economists both have some decent intuition that a falling population makes falling total output more likely. Economists, however, maintain that income per capita is not so certain to fall. After all, both the numerator and denominator of GDP per capita can fall such that the net effect on the entire ratio is a wash or even increase. In fact, aggregate real output can still continue to grow *if* labor productivity rises faster than the rate of employment decline.
But this is a big if. After all, some of the thrust of endogenous growth theory emphasizes that population growth corresponds to more human brains, which results in more innovation when those brains engage with economic problems. Therefore, in the long run, smaller populations innovate more slowly than larger populations. Furthermore, given that information can cross borders relatively easily no one on the globe is insulated from the effects of lower global population. Because information crosses borders relatively well, the brains-to-riches model doesn’t tell us who will innovate more or experience greater productivity growth.
What follows is not the only answer. There are certainly multiple. For example, recent Nobel Prize winner Joel Mokyr says that both basic science *and* knowledge about applications must grow together. That’s not the route that I’ll elaborate.
Continue reading