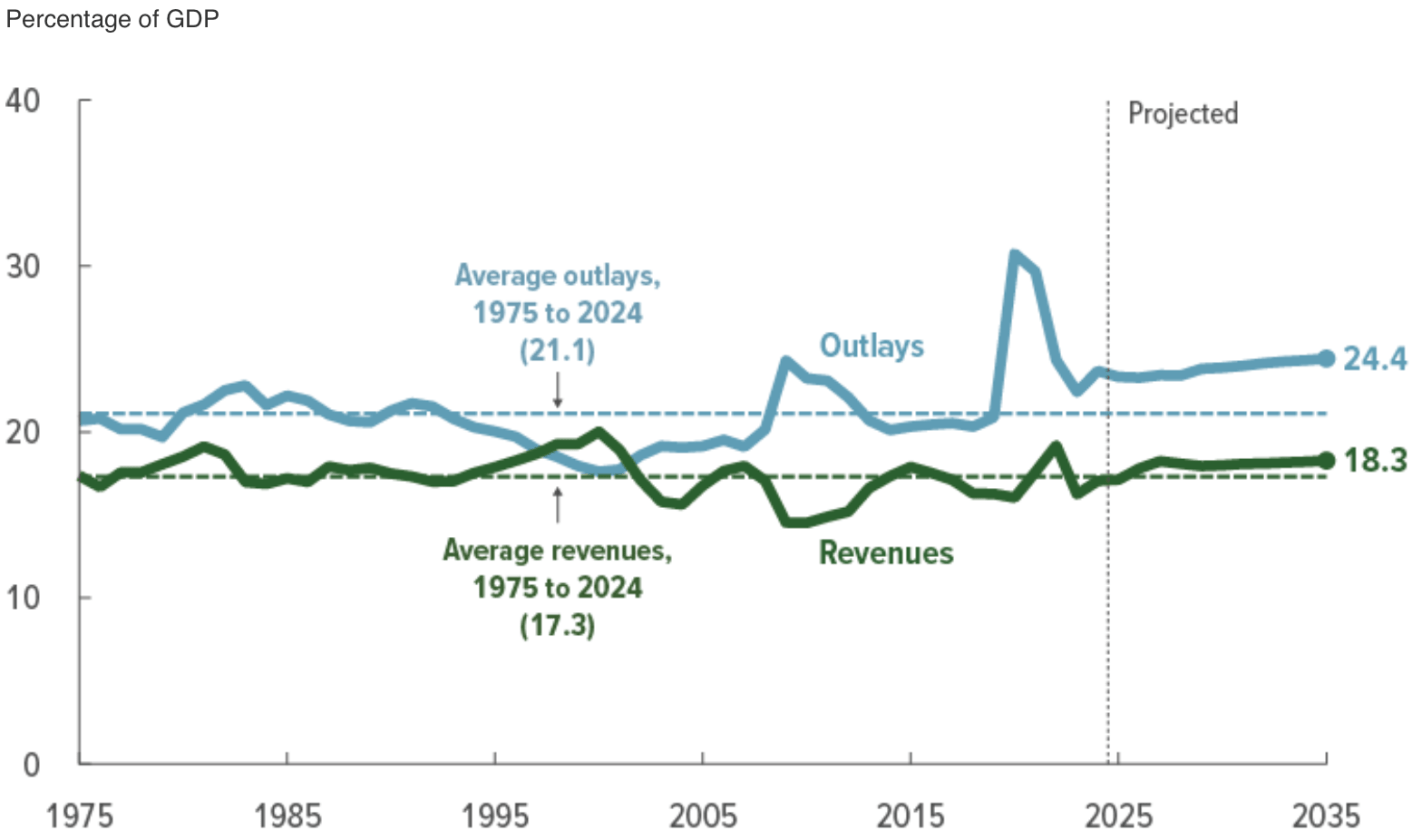
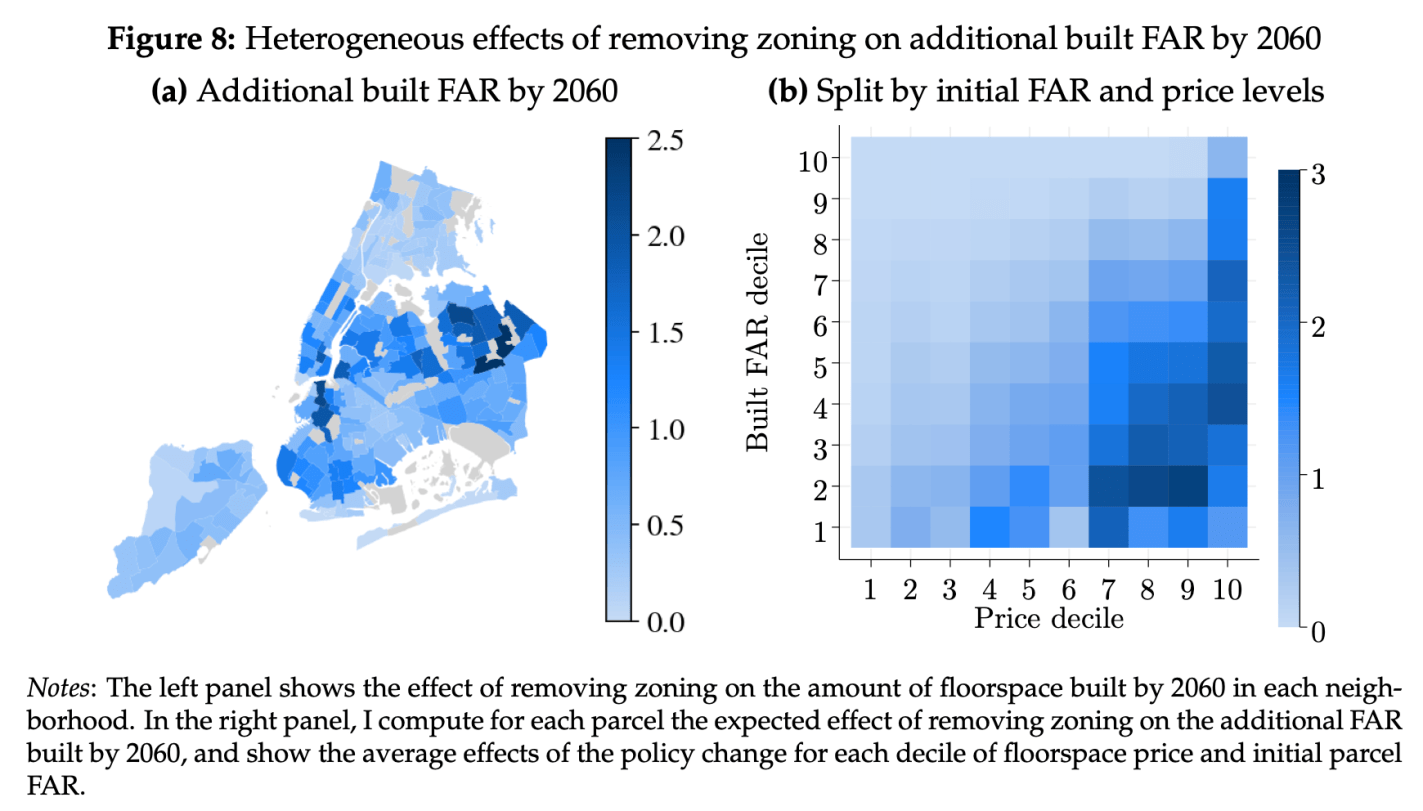
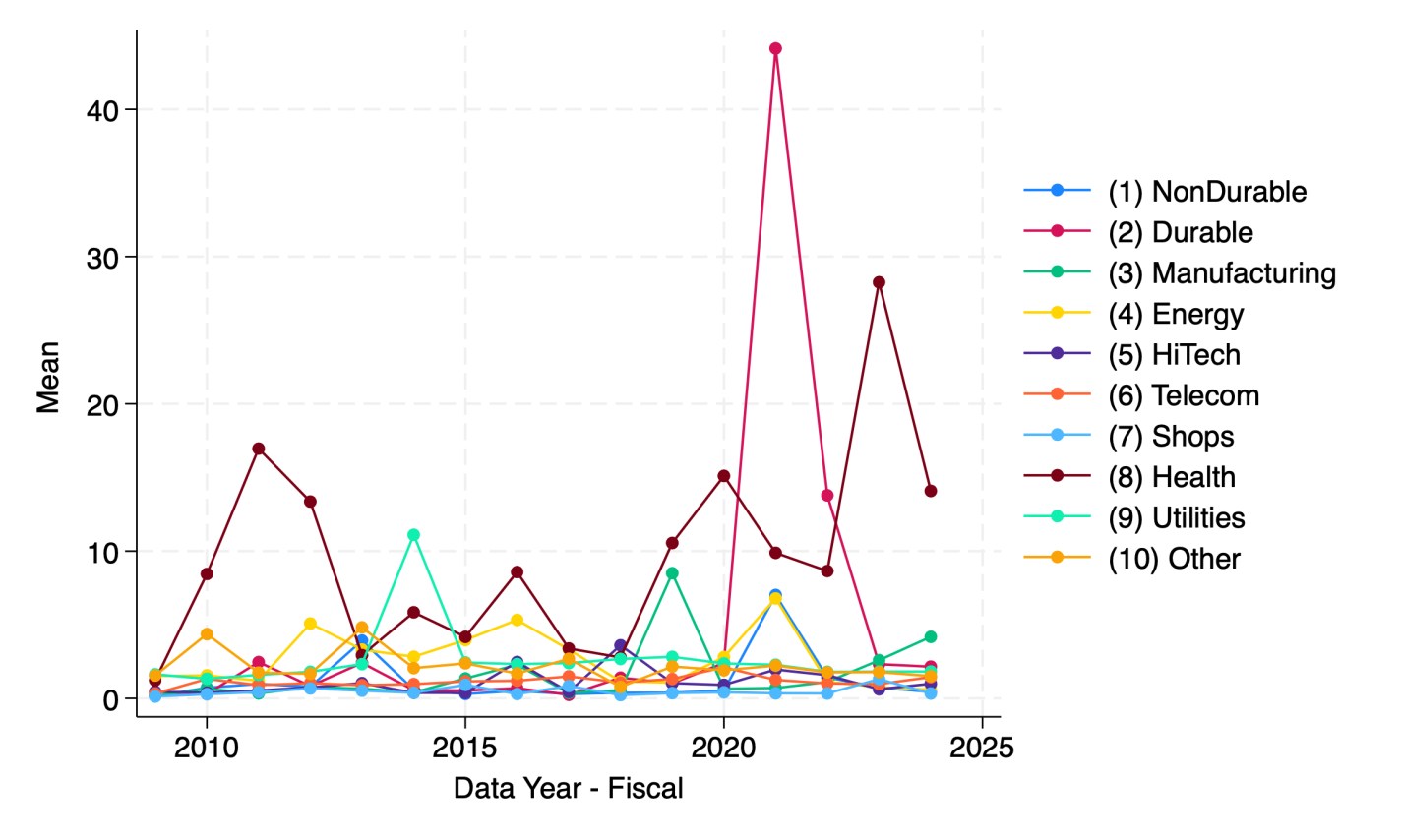
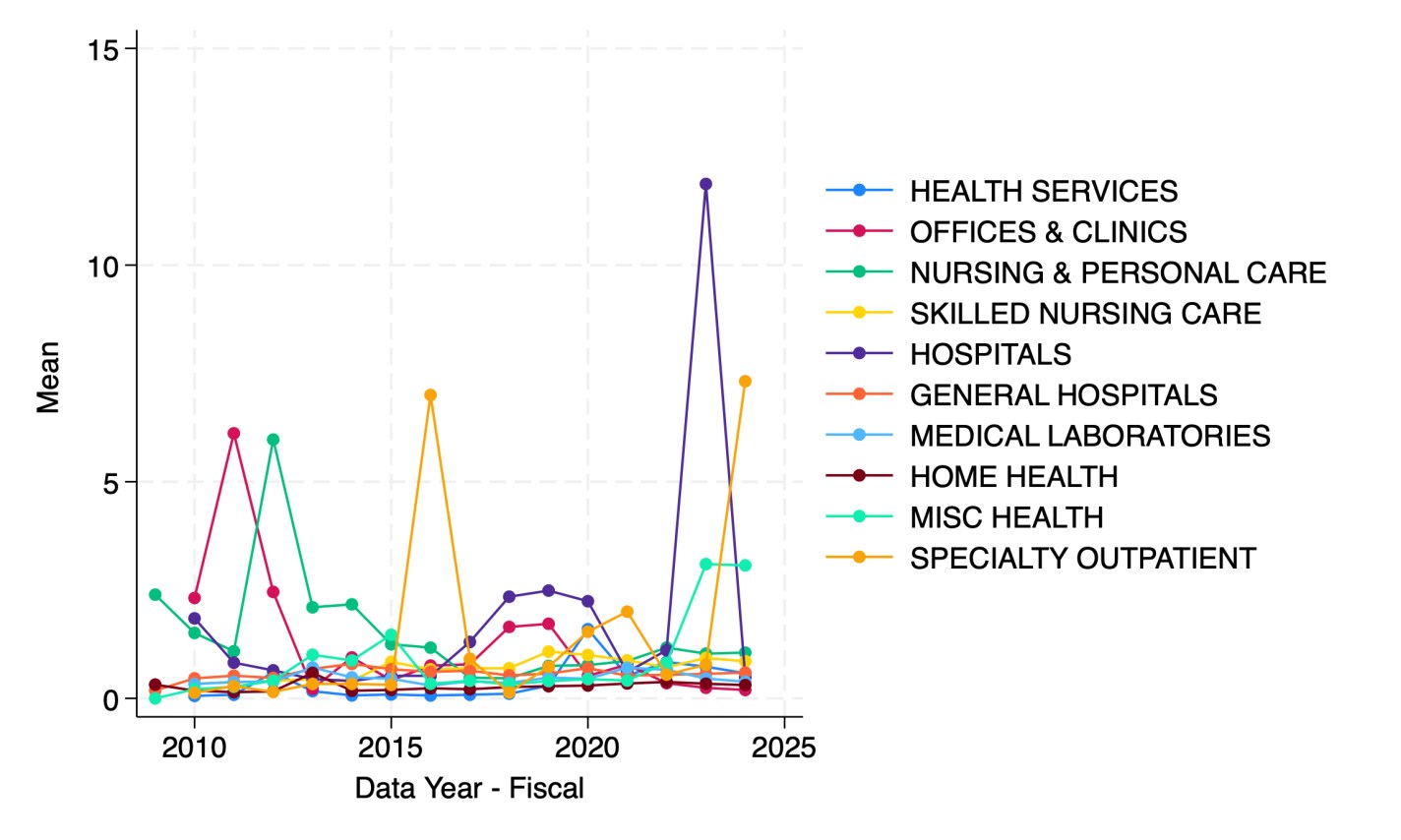
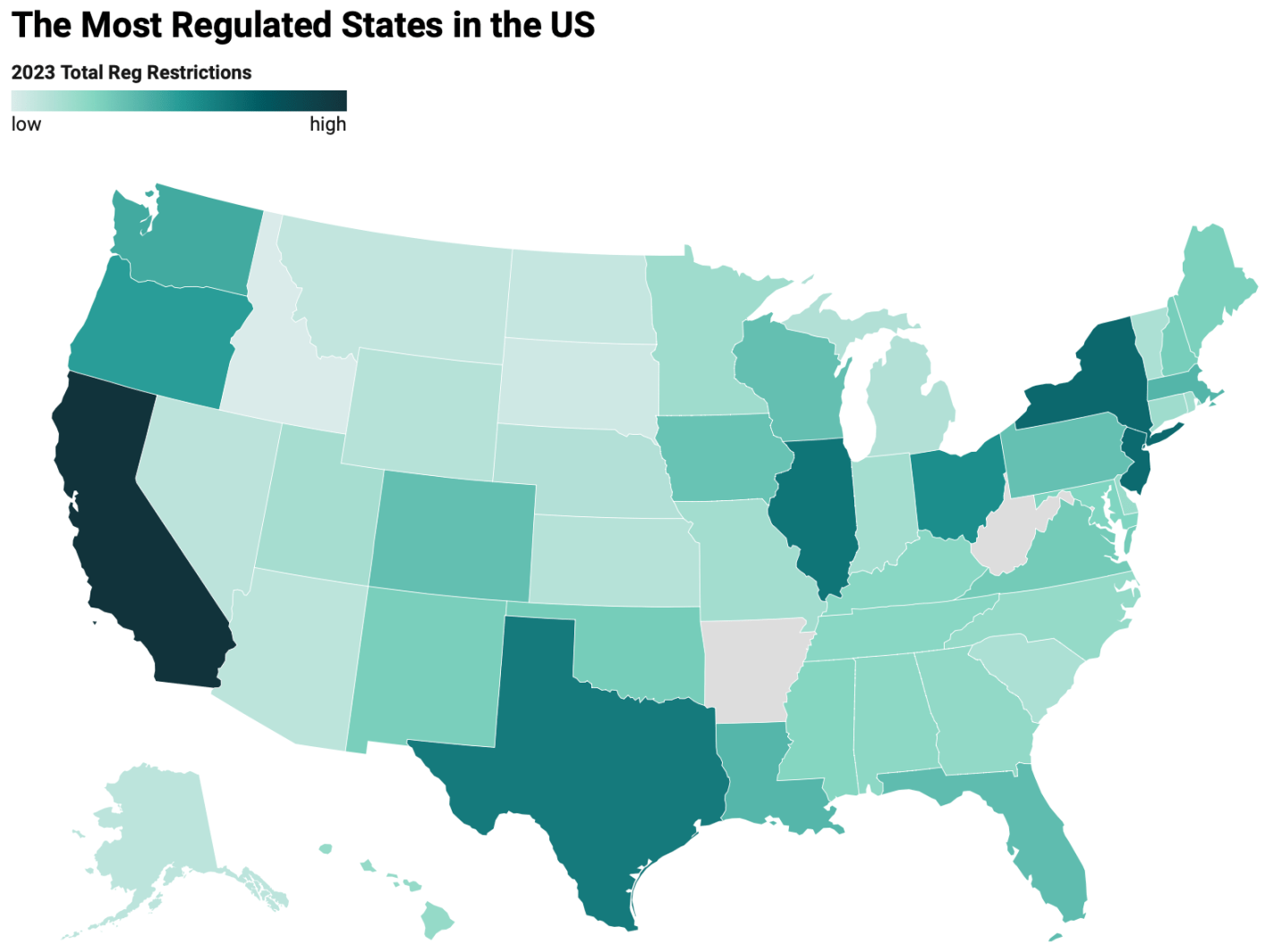
When every frontier AI model can pass your tests, how do you figure out which model is best? You write a harder test.
That was the idea behind Humanity’s Last Exam, an effort by Scale AI and the Center for AI Safety to develop a large database of PhD-level questions that the best AI models still get wrong.
The effort has proven popular- the paper summarizing it has already been cited 91 times since its release on March 31st, and the main AI labs have been testing their new models on the exam. xAI announced today that its new Grok 4 model has the highest score yet on the exam, 44.4%.

The process of creating the dataset is a fascinating example of a distributed academic mega-project, something that is becoming a trend that has also been important in efforts to replicate previous research. The organizers of Humanity’s Last Exam let anyone submit a question for their dataset, offering co-authorship to anyone whose question they accepted, and cash prizes to those who had the best questions accepted. In the end they wound up with just over 1000 coauthors on the paper (including yours truly as one very minor contributor), and gave out $500,000 to contributors of the very best questions (not me), which seemed incredibly generous until Scale AI sold a 49% stake in their company to Meta for $14.8 billion in June.

Here’s what I learned in the process of trying to stump the AIs and get questions accepted into this dataset:
- The AIs were harder than I expected to stump because they used frontier models rather than the free-tier models I was used to using on my own. If you think AI can’t answer your question, try a newer model
- It was common for me to try a question that several models would get wrong, but at least one would still get right. For me this was annoying because questions could only be accepted if every model got them wrong. But of course if you want to get a correct answer, this means trying more models is good, even if they are all in the same tier. If you can’t tell what a correct answer looks like and your question is important, make sure to try several models and see if they give different answers
- Top models are now quite good at interpreting regression results, even when you try to give them unusually tricky tables
- AI still has weird weaknesses and blind spots; it can outperform PhDs in the relevant field on one question, then do worse than 3rd graders on the next. This exam specifically wanted PhD-level questions, where a typical undergrad not only couldn’t answer the question, but probably couldn’t even understand what was being asked. But it specifically excluded “simple trick questions”, “straightforward calculation/computation questions”, and questions “easily answerable by everyday people”, even if all the AIs got them wrong. My son had the idea to ask them to calculate hyperfactorials; we found some relatively low numbers that stumped all the AI models, but the human judges ruled that our question was too simple to count. On a question I did get accepted, I included an explanation for the human judges of why I thought it wasn’t too simple.


I found this to be a great opportunity to observe the strengths and weaknesses of frontier models, and to get my name on an important paper. While the AI field is being driven primarily by the people with the chops to code frontier models, economists still have lot we can contribute here, as Joy has shown. Any economist looking for the next way to contribute here should check out Anthropic’s new Economic Futures Program.