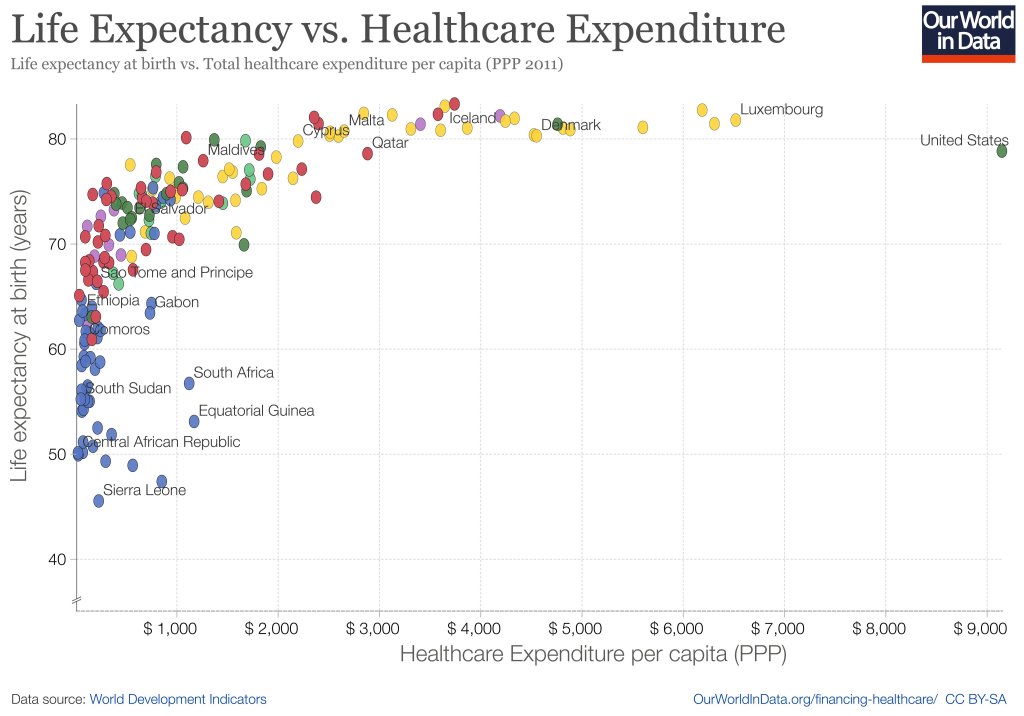
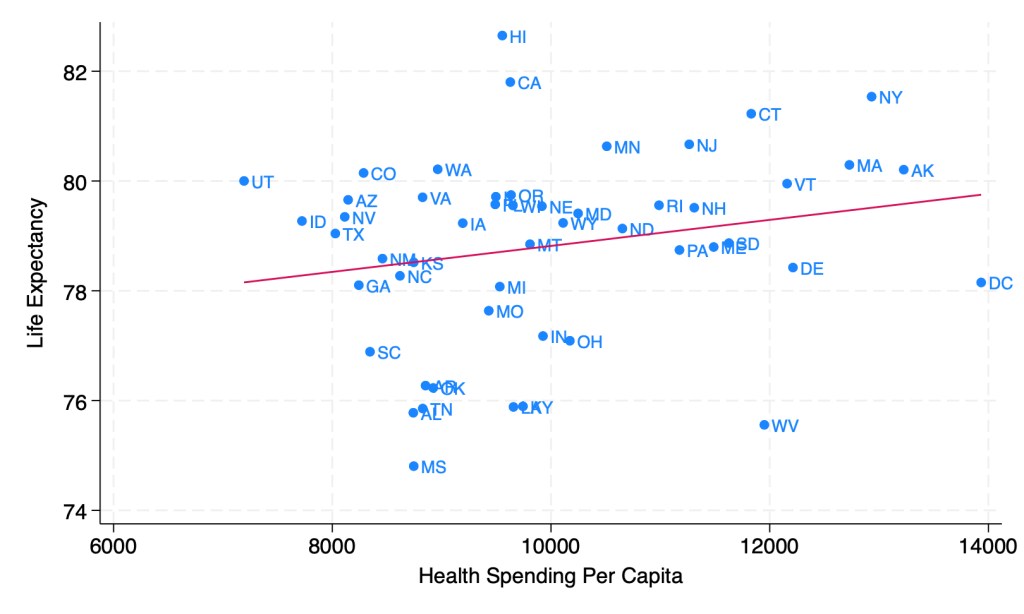
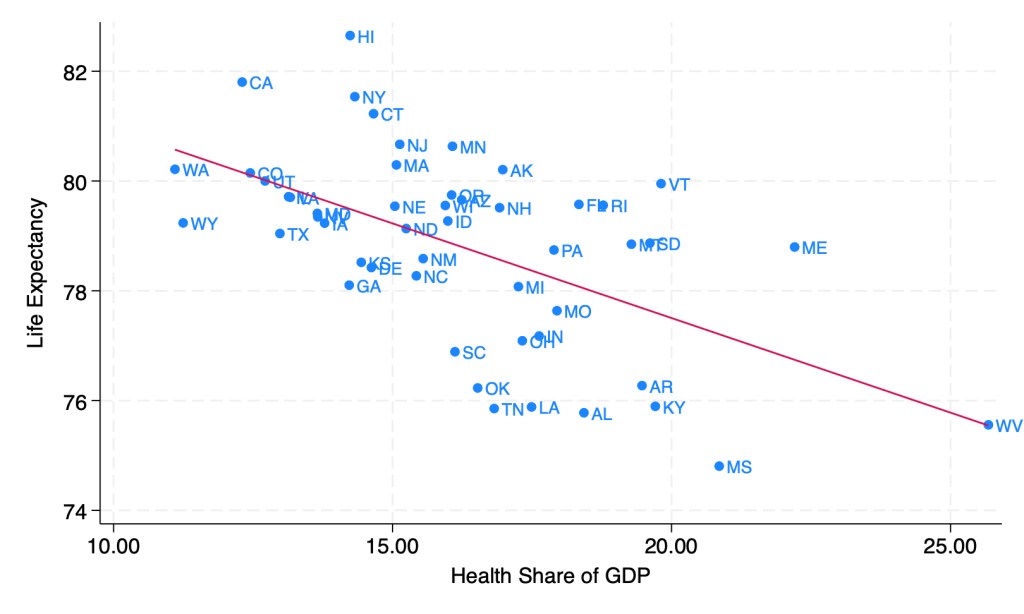
I’m back from Manifest, a conference on prediction markets, forecasting, and the future. It was an incredible chance to hear from many of my favorite writers on the internet, along with the CEOs of most major prediction markets; in Steve Hsu’s words, Woodstock for Nerds. Some highlights:
Robin Hanson took over my session on academic research on prediction markets (in a good way; once he was there everyone just wanted to ask him questions). He thinks the biggest current question for the field is to figure out why is the demand for prediction markets so low. What are the different types of demand, and which is most likely to scale? In a different talk, Robin says that we need to either turn the ship of world culture, or get off in lifeboats, before falling fertility in a global monoculture wrecks it.

Play-money prediction markets were surprisingly effective relative to real-money ones in the 2022 midterms. Stephen Grugett, co-founder of Manifold (the play-money prediction market that put on the conference), admitted that success in one election could simply be a coincidence. He himself was surprised by how well they did in the 2022 midterms, and said he lost a bunch of mana on bets assuming that Polymarket was more accurate.
Substack CEO Chris Best: No one wants to pay money for internet writing in the abstract, but everyone wants to pay their favorite writer. For me, that was Scott Alexander. We are trying to copy Twitter a bit. Wants to move into improving scientific publishing. I asked about the prospects of ending the feud with Elon; Best says Substack links aren’t treated much worse than any other links on X anymore.
Razib Khan explained the strings he had to pull for his son to be the first to get a whole genome sequence in utero back in 2014- ask the hospital to do a regular genetic test, ask them for the sample, get a journalist to tweet at them when they say no, get his PI’s lab to run the sample. He thinks crispr companies could be at the nadir of the hype cycle (good time to invest?).
Kalshi cofounder Luana Lopes Lara says they are considering paying interest on long term markets, and offering margin. There is enough money in it now that their top 10 or so traders are full time (earning enough that they don’t need a job). The CFTC has approved everything we send them except for once (elections). We don’t think their current rule banning contest markets will go through, but if it does we would have to take down Oscar and Grammy markets. When we get tired of the CFTC, we joke that we should self certify shallot futures markets (toeing the line of the forbidden onion futures). Planning to expand to Europe via brokerages. Added bounty program to find rules problems. Launching 30-50 markets per week now (seems like a good opportunity, these can’t all be efficient right?).

There was lots else of interest, but to keep things short I’ll just say it was way more fun and informative doing yet another academic conference, where I’ve hit diminishing returns. More highlights from Theo Jaffee here; I also loved economist Scott Sumner’s take on a similar conference at the same venue in Berkeley:
If you spend a fair bit of time surrounded by people in this sector, you begin to think that San Francisco is the only city that matters; everywhere else is just a backwater. There’s a sense that the world we live in today will soon come to an end, replaced by either a better world or human extinction. It’s the Bay Area’s world, we just live in it.