Back in February, 2023 I wrote an enthusiastic plug for including managed futures funds in an investment portfolio. That was based on several observations. First, bonds have become often positively correlated with stocks, so the traditional 60/40 stock/bond portfolio provides less hedging or diversification than earlier. Second, during the long grinding bear market of Jan-Oct 2022, managed futures funds shot up, nicely hedging stocks. Third, I had only recently discovered managed futures, so they were for me a shiny new toy.
Managed futures funds hold both long and short positions in futures contracts for a variety of commodities (e.g., oil, gas, metals, cattle), stocks (e.g., domestic vs. international) and other financial instruments (domestic and foreign bonds, currencies, interest rates, etc.). Fund managers usually base their positioning on momentum or trend-following. Historical data shows that if a commodity moves up steadily for, say, a month, there is greater than 50% odds that it will continue moving up for some additional time. If the fund’s positioning is correct, it makes money the next week or month. If it is incorrect, the fund loses money.
Historically, a good managed futures fund will trade fairly flat or slightly up during a stock bull phase, then step up to give positive return during a stock bear market, to counter the drop in equities prices. We can see below how that worked for managed future (MF) ETF KMLM around 2022. It rose slowly in 2021, then fell back at the end of the year. However, in Jan-Oct 2022 while stocks (and bonds) were painfully grinding down to a 22% loss, KMLM ripped higher by a huge 40%. That seems like a great hedge:
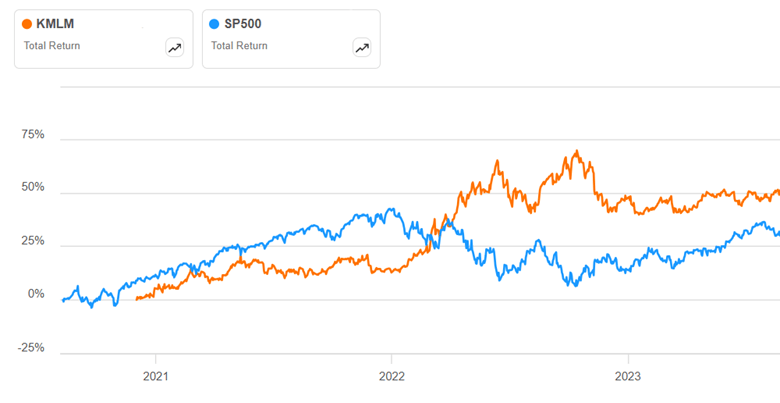
KMLM quickly gave back those gains, for reasons we will discuss. But if you had been consistently rebalancing your portfolio, you would have captured much of those gains.
This sort of performance is why some advisors recommend moving much of your non-stock holdings out of bonds and into managed futures. What’s not to like here?
It turns out that MF funds struggle if there are not fairly long, strong trends in commodity prices. If trends reverse quickly, and then reverse again, then the fund’s positions will lose money over and over. We can see this in the above plot. The story for most of 2022 was interest rates going up and up and up. MF funds were rock stars as they rode that trend for many months. But there was a surprising break in futures trends in November, 2022, as markets suddenly started pricing in an early Fed pivot towards easing in 2023, and so interest rates rose, and bonds and the U.S. dollar tumbled. All the managed futures funds took a sharp hit Nov-Dec 2022. KMLM then went roughly flat for 2023; other MF funds fared worse.
So far, so good. However, it seems like there has been a sea change in futures markets. Before around 2010 or so, there is reason to believe that much of the futures price action was driven by the underlying commodities themselves. For instance, cattle or soybean producers wanted to protect themselves against changes in cattle or soy prices, and so they would buy or sell futures to lock in prices say eight months out. In these situations, there would naturally and normally be months-long trends in futures prices. Wall Street took the other side of those trades. But now it seems to me (can’t give proof reference) that it’s speculators on both sides of the trades, leading to trade algos constantly trying to outguess each other and higher volatility.
For whatever reason, normal trend-following MF has been a bad business for the past 2 years. Here is a continuation of the chart above, showing mid Aug 2023- mid Aug 2025 for KMLM (orange line) compared to S&P 500 stocks (blue line):
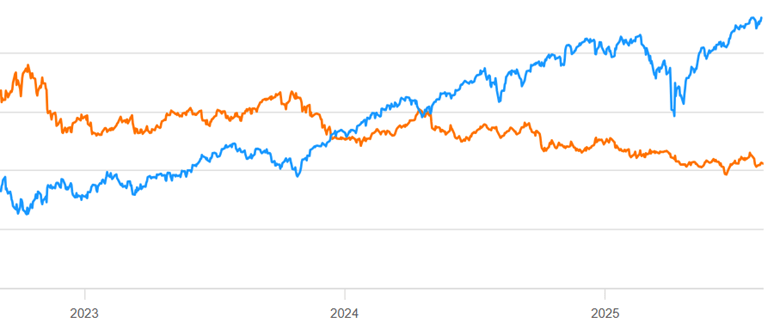
The scale is not shown here, but KMLM lost some 30% of its value during that time period. That is NOT the kind of hedge you want to hold.
So, should we forget about MF funds? It turns out that not all MF funds perform the same. My informal research suggests that most MF funds have performed similar to KMLM in the past two years (=abysmally). Since my 2023 article, though, (a) an improved MF ETF (CTA) has appeared, and (b) I became aware of a superior MF fund (AQMNX) of the old-style (non-ETF) mutual fund format. Below is a 3-year chart of KMLM, SP500, and the ETF CTA and the mutual fund AQMNX:
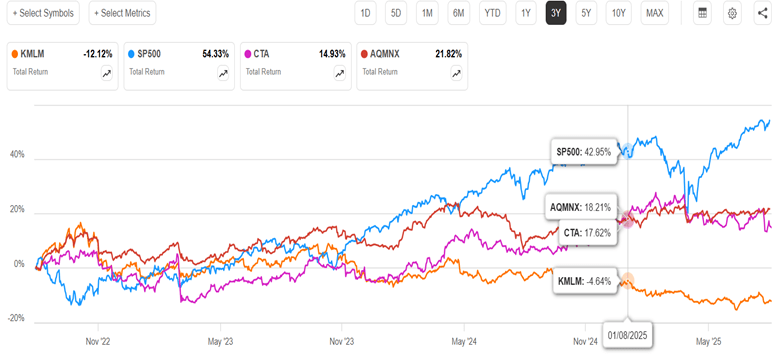
We can see that both the new contenders are up instead of down in the past three years, and both were uncorrelated enough to SP500 to cushion the big Feb-April stock drawdown this year. They handily outperformed bonds (e.g. BND, not shown) during this time period.
There are fundamental reasons why those two funds would behave differently than plain vanilla trend-following KMLM. CTA adds a factor called carry (which I will not try to define) to its algo, and also takes large concentrated bets. AQMNX draws on the very sophisticated quantitative resources of the AQM fund family. It also takes long/short bets on equities (e.g. S&P 500 index), which are not in KMLM. AQMNX is not available through all brokerages (it is at Fidelity).
As the months roll by and plain stocks soar effortlessly up and up, it may seem pointless to consider any portfolio hedges. But for those who value diversification, these two funds may merit consider consideration. (As usual, nothing here should be considered advice to buy or sell any security).








