A periodically recurring conversation on social media is whether imports are bad for GDP. Everyone thinks they are clearly right, and then they lazily defer to brief dismissal of the opposing view. Some of this might be due to media format. Something just a tiny bit more thorough could help to resolve the painfully unproductive online interactions… And just maybe improve understanding.
It starts with the GDP expenditure identity:

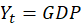
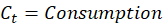
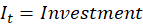

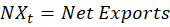
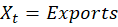
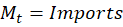
The initial assertion is that imports reduce GDP. After all, M enters the equation negatively. So, all else constant, an increase in M reduces Y. It’s plain and simple.
Many economists reply that the equation is an accounting identity and not a theory about how the world works and that the above logic is simply confusing these two things. This reply 1) allows its employers to feel smart, 2) doesn’t address the assertion, & 3) doesn’t resolve anything. In fact, this reply erects a wall of academic distinction that prevents a resolution. What a missed opportunity to perform the literal job of “public intellectual”.
How are Imports Bad/Good/Irrelevant for GDP?
Let’s add a small but important detail to the above equation to distinguish between consumption of goods produced domestically and those produced elsewhere.
Continue reading