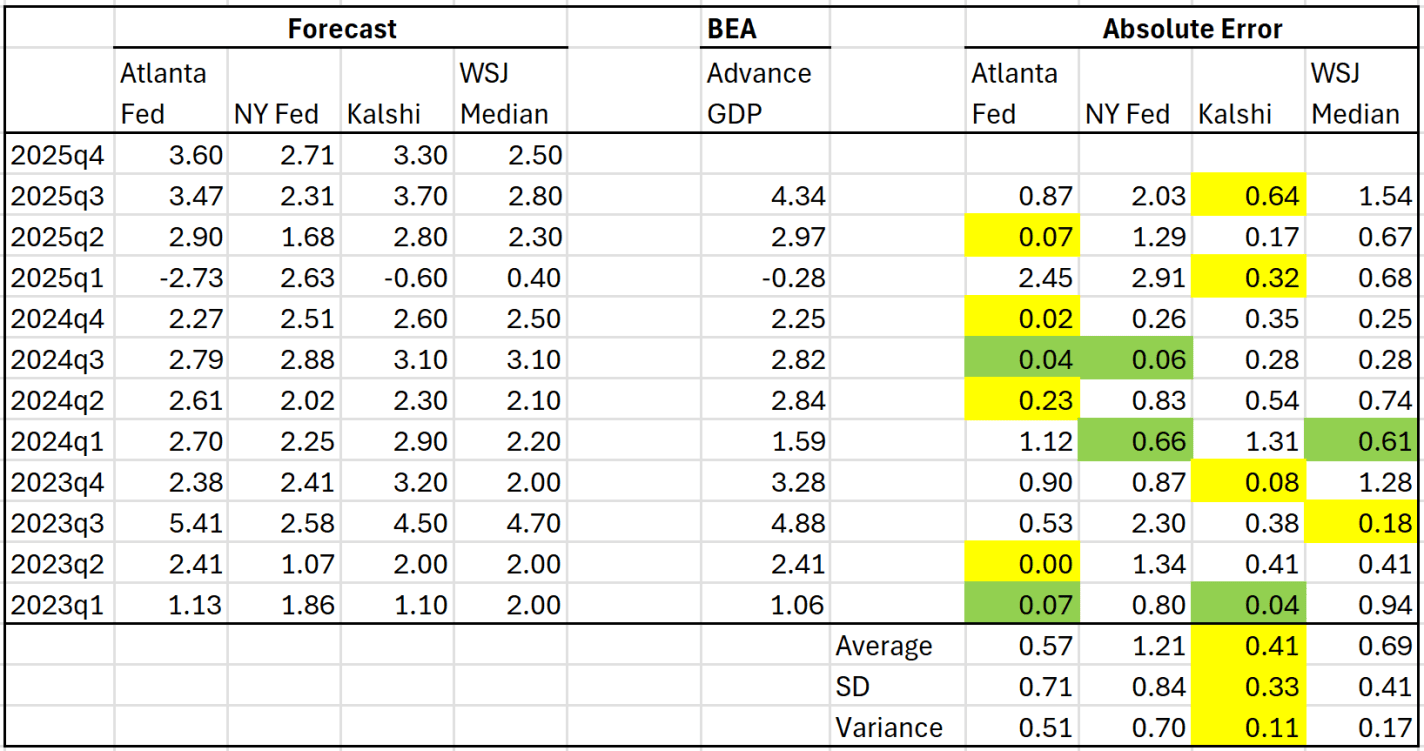
Autism is a condition that can cause enormous anxiety and grief, especially for parents of autistic children. The economic implications are also considerable. A 2021 study by Blaxill, et al., estimated the annual costs to society of autism in the U.S. to be $223 billion in 2020, $589 billion in 2030, $1.36 trillion in 2040, and an astonishing $5.54 trillion by 2060.
The rising diagnosis rates are sometimes attributed to changes in environmental factors or diets. It is obviously essential to get the science right on this. Here I will summarize an article by epidemiologist Mark Strand, “Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder Epidemiologically and Theologically”. This article was published on the Biologos web site on January, 2026. The author addresses the medical aspects sand also the moral aspects. Upfront disclaimer: I have no expertise in this area; I am just trying to faithfully convey the scientific consensus.
The Myth of the “Autism Epidemic”
The article begins by addressing a common misconception: that autism is experiencing a sudden, alarming surge in cases—an “epidemic.” This idea gained traction when the current administration announced a “massive testing and research effort” to identify environmental causes behind the rise. But as the author explains, this framing is scientifically inaccurate.
Autism is not an acute condition like strep throat or a viral outbreak. It’s a lifelong neurodevelopmental disorder that emerges during early brain development, typically between ages two and four. Unlike infectious diseases that appear suddenly and resolve quickly, autism is chronic and complex. The term “epidemic” refers to a rapid, atypical increase in cases—something that doesn’t align with the actual data.
In 2022, the CDC’s Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (ADDM) Network reported 32.2 cases of ASD per 1,000 children. This is massive (fourfold) increase from two decades ago. But this rise isn’t due to a sudden environmental trigger. Instead, it reflects broader diagnostic criteria, increased public awareness, better screening practices, and greater access to services:
While this increase may seem alarming at first glance, it is widely accepted that it largely reflects changes in the definition used for ASD and the importance placed on ASD by society and educational systems.
Since it was first recognized as a condition in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM), the definition for ASD has been broadened several times. This included combining a cluster of related neurological disorders into one disorder, relaxing the age of onset, and better classifying the presentation of autism in girls and children of color, leading to more accurate, but higher, numbers.
States like California and Pennsylvania, which have robust early intervention systems and strong Medicaid coverage for autism services, report the highest prevalence rates.
Genetics Over Environment: The Scientific Consensus
One of the most critical points the article makes is that autism is primarily genetic. Twin studies show that if one identical twin has autism, the other twin has a 60% to 90% chance of also having it. A large Swedish study of over 37,000 twins found that 83% of autism cases could be attributed to genetics.
While environmental factors may play a role, the evidence is far from conclusive. The article debunks popular myths—like the claim that acetaminophen (Tylenol) use during pregnancy causes autism. High-quality studies, including one of 2.5 million children in Sweden with sibling controls, found no link between prenatal acetaminophen use and autism risk. Similarly, the idea that vaccines cause autism has been thoroughly discredited by decades of rigorous research.
The real danger lies in chasing unproven causes—a practice that wastes resources and distracts from meaningful science. Instead, researchers should focus on gaps in knowledge using the scientific method: building on what we know, forming new hypotheses, and testing them rigorously.
The Spectrum of Experience: Diversity, Not Deficit
Autism is not a monolithic condition. It exists on a spectrum, ranging from individuals with significant support needs to those with high intelligence and exceptional skills.
The article highlights some striking statistics:
- 14% of autistic individuals graduate from college, compared to 32% of the general population.
- Among college graduates with autism, 34.3% major in STEM fields, significantly higher than the 22.8% in the general population.
These numbers challenge the harmful stereotype that autistic people are universally disabled or burdensome. Many autistic individuals thrive in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics—fields that value pattern recognition, attention to detail, and deep focus.
Yet, challenges remain. Social communication difficulties, restricted interests, and repetitive behaviors can be isolating. Early intervention—especially for those with moderate to mild autism—can make a meaningful difference in socialization and quality of life.
A Call for Grace, Truth, and Inclusion
The article concludes by noting that autism is not a tragedy, but a part of human diversity. It calls on society at large to respond with truth, grace, and care—not fear or stigma.
The article notes: “It is not a good use of resources to repeat studies on well-established scientific evidence or chase popular beliefs about supposed causes.” Rather than searching for a single cause to “eliminate,” we should focus on understanding, supporting, and empowering autistic people. This includes investing in early screening, improving access to therapy, and promoting inclusive education and employment.
The rise in autism diagnoses is not a crisis to panic about—it’s a call to do better with better science, better policies, and better compassion. By grounding our understanding in data, embracing neurodiversity, and responding with love, we can build a world where autistic individuals are not just accepted—but valued.
MORE ON GENETIC CAUSATION OF AUTISM
I was curious, so I did a little more digging, beyond Dr. Strand’s article, on the roots of autism. Here are couple of quotes from the UCLA David Geffen School of Medicine, home of Dr. Daniel Geschwind, who won a National Academy of Medicine prize for investigating autism’s genetic underpinnings:
Autism is hereditary and therefore does run in families. A majority (around 80%) of autism cases can be linked to inherited genetic mutations. The remaining cases likely stem from non-inherited mutations.
There’s no evidence that children can develop autism after early fetal development as a result of exposure to vaccines or postnatal toxins. “Everything known to cause autism occurs during early brain development,” says Dr. Geschwind.
A NOTE ON TREATMENTS FOR AUTISM
Some articles on autism seem to convey that it is a condition that someone is simply stuck with for the rest of their lives, with maybe a brief nod to “therapies”. But this situation is maybe not quite so grim, at least for some children on the spectrum. My browser AI summarizes the situation as:
Therapy for autism can be highly effective, particularly when started early and tailored to the individual’s needs. Evidence-based therapies such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), speech therapy, occupational therapy (OT), and physical therapy (PT) are widely recognized for improving communication, social skills, daily living abilities, and reducing challenging behaviors.
And, anecdotally, I know a board-certified behavior analyst (BCBA) who has reported seeing significant improvements with autistic children upon treatment. Early, skilled therapy can often reshape a child’s behavioral habits enough to allow them to function in mainstream society.