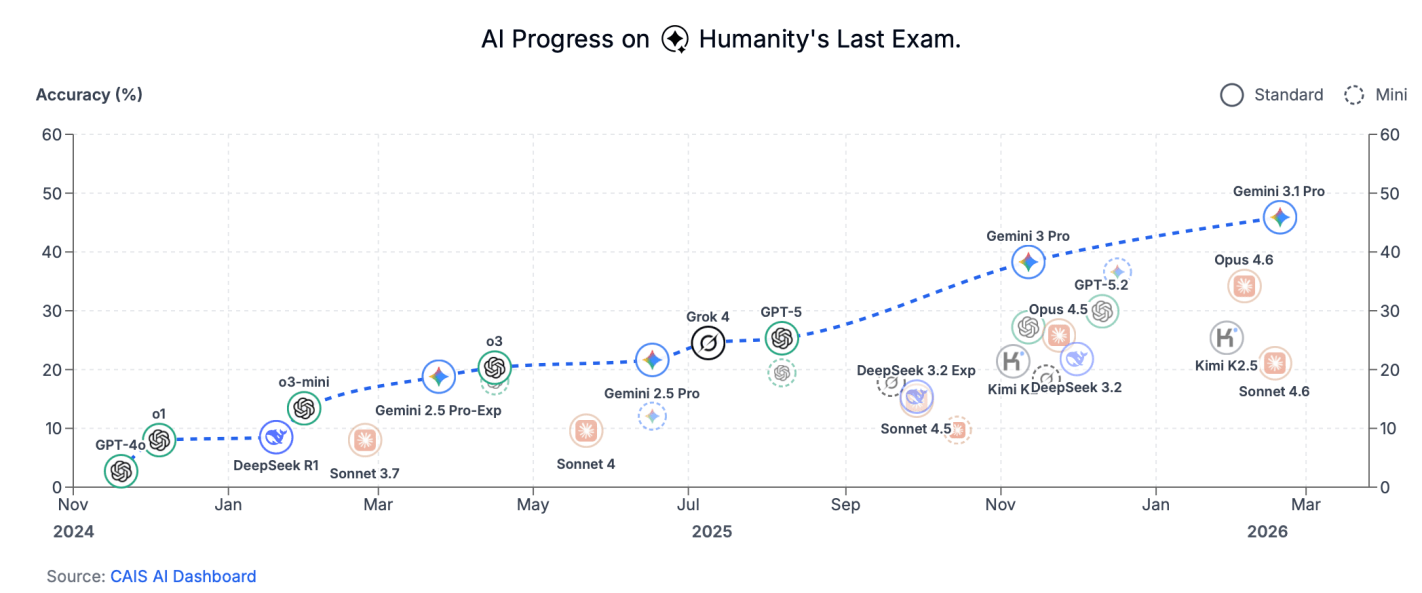
A tsunami of sentiment shift is washing over Wall Street, away from Nvidia and towards Google/Alphabet. In the past month, GOOG stock is up a sizzling 12%, while NVDA plunged 13%, despite producing its usual earnings beat. Today I will discuss some of the technical backdrop to this sentiment shift, which involves the differences between training AI models versus actually applying them to specific problems (“inference”), and significantly different processing chips. Next week I will cover the company-specific implications.
As most readers here probably know, the popular Large Language Models (LLM) that underpin the popular new AI products work by sucking in nearly all the text (and now other data) that humans have ever produced, reducing each word or form of a word to a numerical token, and grinding and grinding to discover consistent patterns among those tokens. Layers of (virtual) neural nets are used. The training process involves an insane amount of trying to predict, say, the next word in a sentence scraped from the web, evaluating why the model missed it, and feeding that information back to adjust the matrix of weights on the neural layers, until the model can predict that next word correctly. Then on to the next sentence found on the internet, to work and work until it can be predicted properly. At the end of the day, a well-trained AI chatbot can respond to Bob’s complaint about his boss with an appropriately sympathetic pseudo-human reply like, “It sounds like your boss is not treating you fairly, Bob. Tell me more about…” It bears repeating that LLMs do not actually “know” anything. All they can do is produce a statistically probably word salad in response to prompts. But they can now do that so well that they are very useful.*
This is an oversimplification, but gives the flavor of the endless forward and backward propagation and iteration that is required for model training. This training typically requires running vast banks of very high-end processors, typically housed in large, power-hungry data centers, for months at a time.
Once a model is trained (e.g., the neural net weights have been determined), to then run it (i.e., to generate responses based on human prompts) takes considerably less compute power. This is the “inference” phase of generative AI. It still takes a lot of compute to run a big program quickly, but a simpler LLM like DeepSeek can be run, with only modest time lags, on a high end PC.
GPUs Versus ASIC TPUs
Nvidia has made its fortune by taking graphical processing units (GPU) that were developed for massively parallel calculations needed for driving video displays, and adapting them to more general problem solving that could make use of rapid matrix calculations. Nvidia chips and its CUDA language have been employed for physical simulations such as seismology and molecular dynamics, and then for Bitcoin calculations. When generative AI came along, Nvidia chips and programming tools were the obvious choice for LLM computing needs. The world’s lust for AI compute is so insatiable, and Nvidia has had such a stranglehold, that the company has been able to charge an eye-watering gross profit margin of around 75% on its chips.
AI users of course are trying desperately to get compute capability without have to pay such high fees to Nvidia. It has been hard to mount a serious competitive challenge, though. Nvidia has a commanding lead in hardware and supporting software, and (unlike the Intel of years gone by) keeps forging ahead, not resting on its laurels.
So far, no one seems to be able to compete strongly with Nvidia in GPUs. However, there is a different chip architecture, which by some measures can beat GPUs at their own game.
NVIDIA GPUs are general-purpose parallel processors with high flexibility, capable of handling a wide range of tasks from gaming to AI training, supported by a mature software ecosystem like CUDA. GPUs beat out the original computer central processing units (CPUs) for these tasks by sacrificing flexibility for the power to do parallel processing of many simple, repetitive operations. The newer “application-specific integrated circuits” (ASICs) take this specialization a step further. They can be custom hard-wired to do specific calculations, such as those required for bitcoin and now for AI. By cutting out steps used by GPUs, especially fetching data in and out of memory, ASICs can do many AI computing tasks faster and cheaper than Nvidia GPUs, and using much less electric power. That is a big plus, since AI data centers are driving up electricity prices in many parts of the country. The particular type of ASIC that is used by Google for AI is called a Tensor Processing Unit (TPU).
I found this explanation by UncoverAlpha to be enlightening:
A GPU is a “general-purpose” parallel processor, while a TPU is a “domain-specific” architecture.
The GPUs were designed for graphics. They excel at parallel processing (doing many things at once), which is great for AI. However, because they are designed to handle everything from video game textures to scientific simulations, they carry “architectural baggage.” They spend significant energy and chip area on complex tasks like caching, branch prediction, and managing independent threads.
A TPU, on the other hand, strips away all that baggage. It has no hardware for rasterization or texture mapping. Instead, it uses a unique architecture called a Systolic Array.
The “Systolic Array” is the key differentiator. In a standard CPU or GPU, the chip moves data back and forth between the memory and the computing units for every calculation. This constant shuffling creates a bottleneck (the Von Neumann bottleneck).
In a TPU’s systolic array, data flows through the chip like blood through a heart (hence “systolic”).
- It loads data (weights) once.
- It passes inputs through a massive grid of multipliers.
- The data is passed directly to the next unit in the array without writing back to memory.
What this means, in essence, is that a TPU, because of its systolic array, drastically reduces the number of memory reads and writes required from HBM. As a result, the TPU can spend its cycles computing rather than waiting for data.
Google has developed the most advanced ASICs for doing AI, which are now on some levels a competitive threat to Nvidia. Some implications of this will be explored in a post next week.
*Next generation AI seeks to step beyond the LLM world of statistical word salads, and try to model cause and effect at the level of objects and agents in the real world – – see Meta AI Chief Yann LeCun Notes Limits of Large Language Models and Path Towards Artificial General Intelligence .
Standard disclaimer: Nothing here should be considered advice to buy or sell any security.