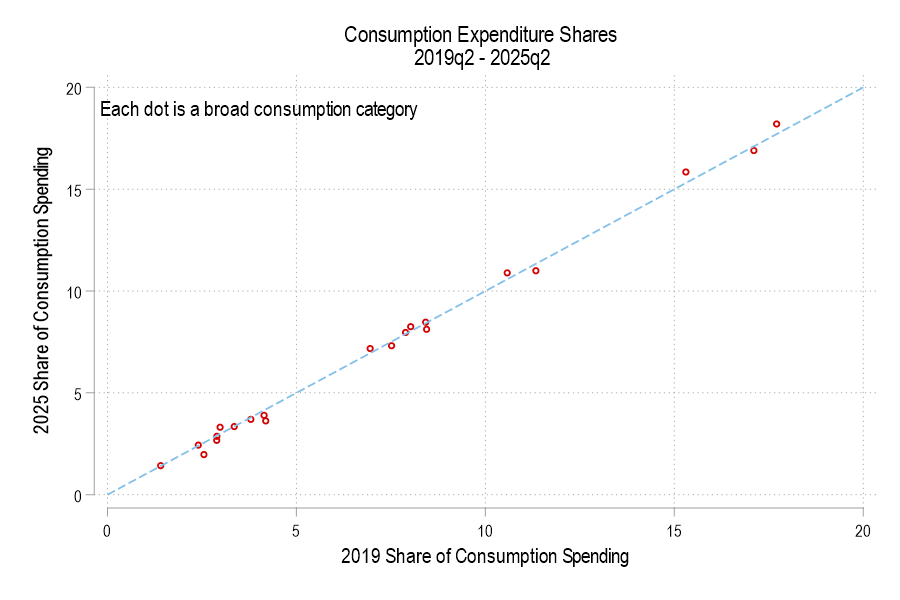
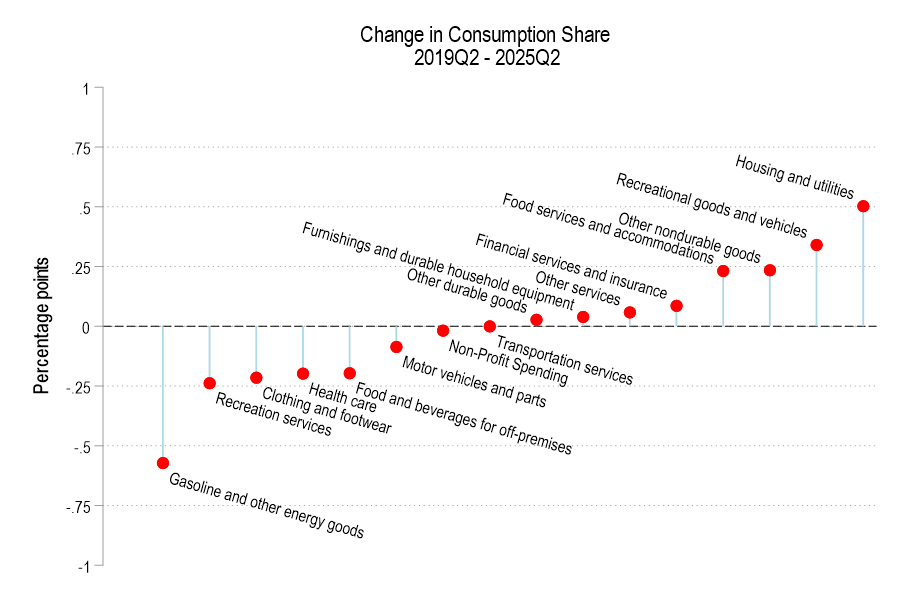
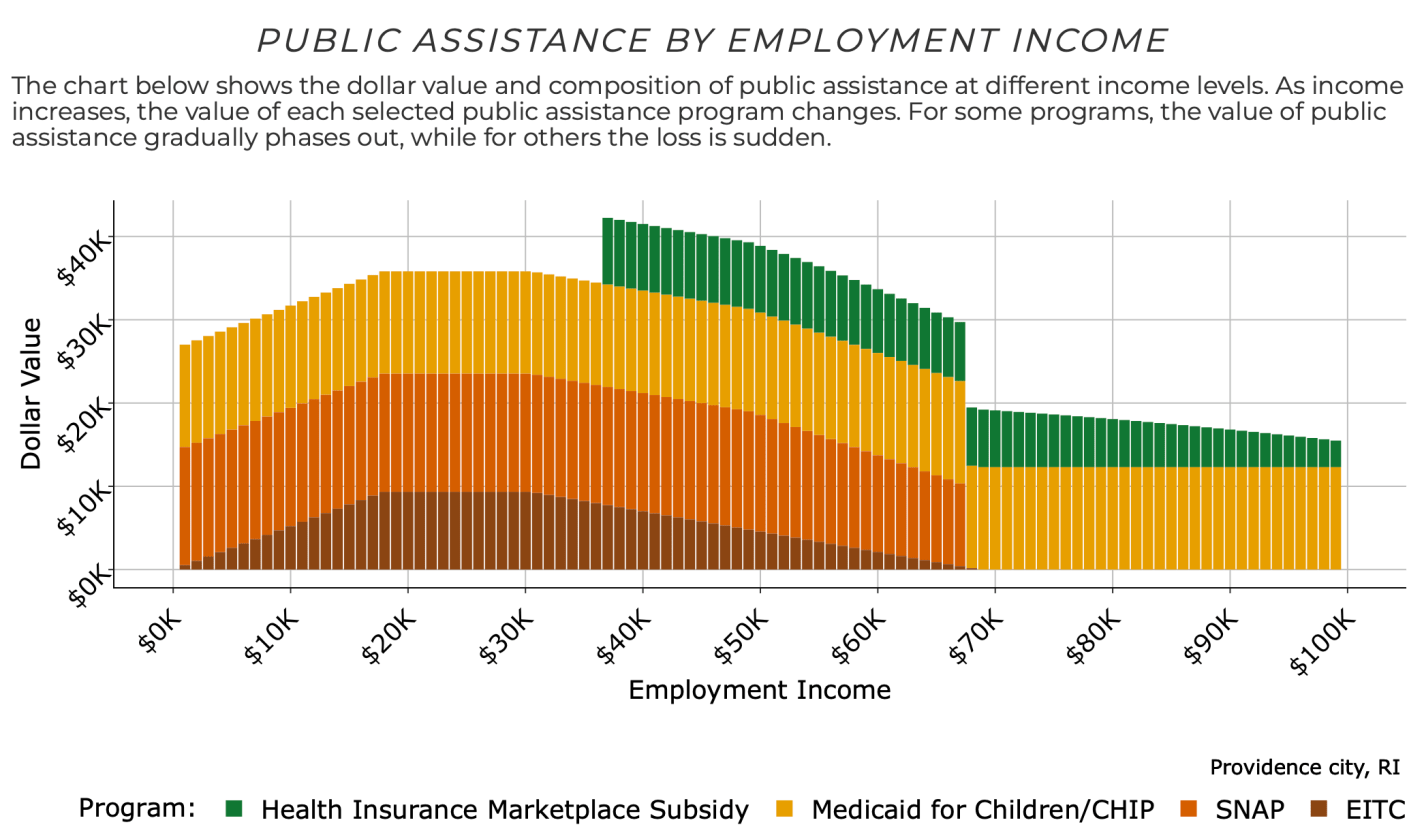
Have you ever looked up and wondered where the time went? One moment you’re living your life, and the next moment you realize that you’ve just lost time that you’ll never get back? That’s what happened to Japan’s economy at the turn of the century in an episode that’s known as ‘the lost decades’. It was a period of slow or null economic growth. Economists differ with their explanations. One cause was the prevalence of ‘zombie firms’.
Japan’s Economy
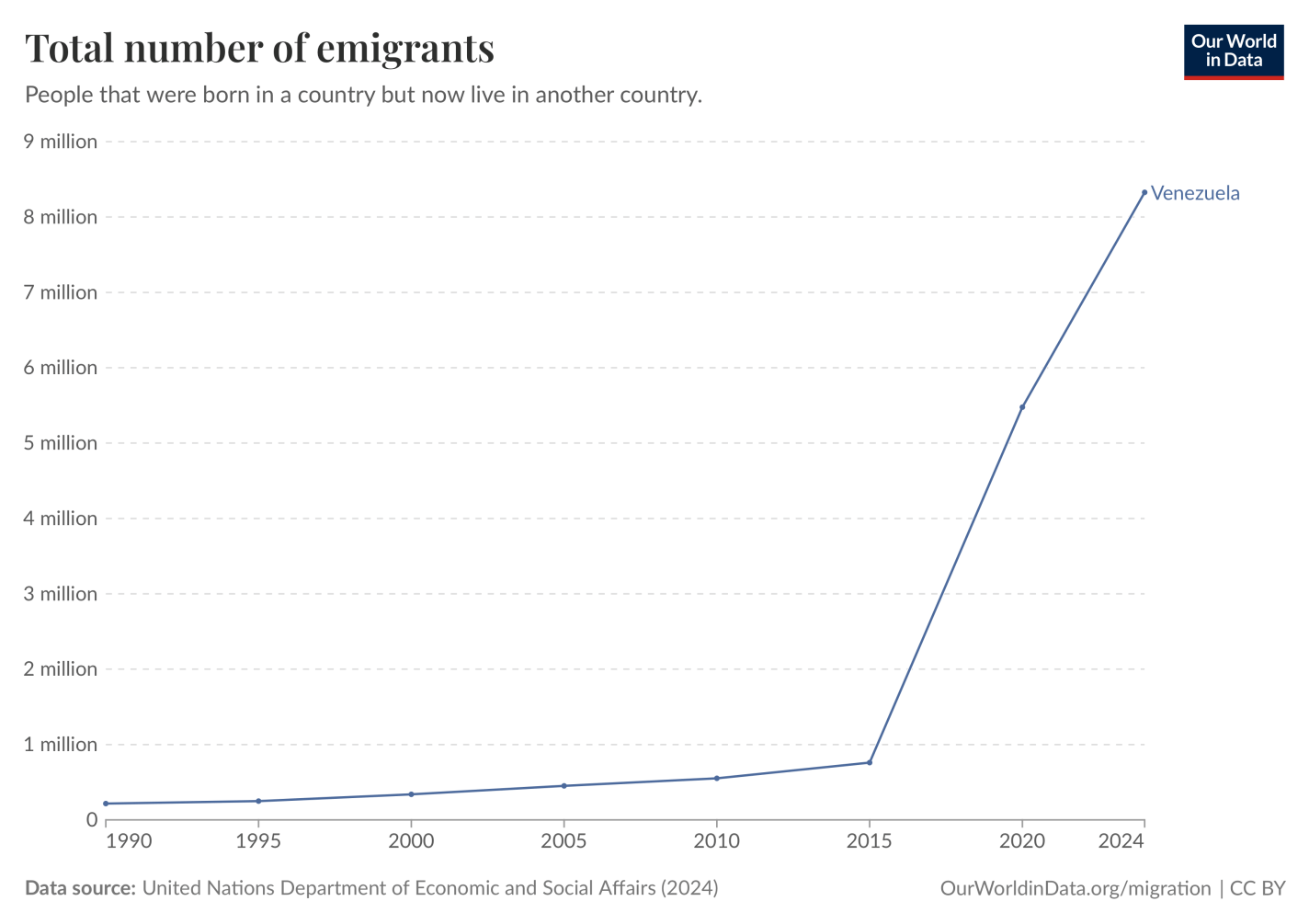
Japan had a current account surplus from 1980-2020, which means that they had more savings than they effectively utilized domestically. Metaphorically, they were so full of savings that they exhausted productive domestic investment opportunities and their savings spilled out into other counties in the form of foreign investments. This was driven by high household savings and slow growth in domestic investment demand. The result was the Japanese firms had easy access to credit. Maybe a little too easy…
Private corporate debt ballooned throughout the 1980s. That’s not intrinsically a problem. In the 1990s, households began saving somewhat less, and most firms began to drastically deleverage… But not all firms. The net effect of the mass deleveraging was that interest rates fell. The firms that remained in debt were the ones that risked insolvency. Less productive firms had slim profits and their Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) was slim. So slim, that they couldn’t pay their debts. Faced with the prospect of insolvency, firms did what was sensible. They refinanced at the lower interest rates. Firms went to their banks and to bond markets and rolled over their debt, which they couldn’t afford, and replaced it with debt that had a lower interest rate. This occurred across industries, but especially in non-tradable goods and services that were insulated from international competition. Crisis averted.
Except this process of refinancing, while avoiding acute defaults and a potential financial crises, ensured that the less productive firms would survive. Not exactly failing and not exactly thriving, they could sort of just hold on to something that looks like life. Well, high debt and low profits aren’t much of a life for a firm. It’s more like being undead – like a zombie. Between 1991 and 1996, the share of non-finance firm assets held by zombie firms ballooned from 3% to 16%. The run-up differed by industry: Manufacturing zombie assets rose from 2% to 12%, from 5% to 33% in real estate, and from 11% to 39% in services. These zombie firms linger on, tying up valuable resources with low-productivity activities and drag on the economy.
China’s Economy
I’m not prone to China hysteria generally. However, I do have uncertainty about the plans and actions of the Chinese government because I don’t know that domestic economic welfare is its priority. That makes forecasting more political and less economic and outside my expertise. Regardless, the Chinese economy is a constraint on the government, whether they like it or not. And there are some echoes of the Japanese economy’s lost decades.
Continue reading