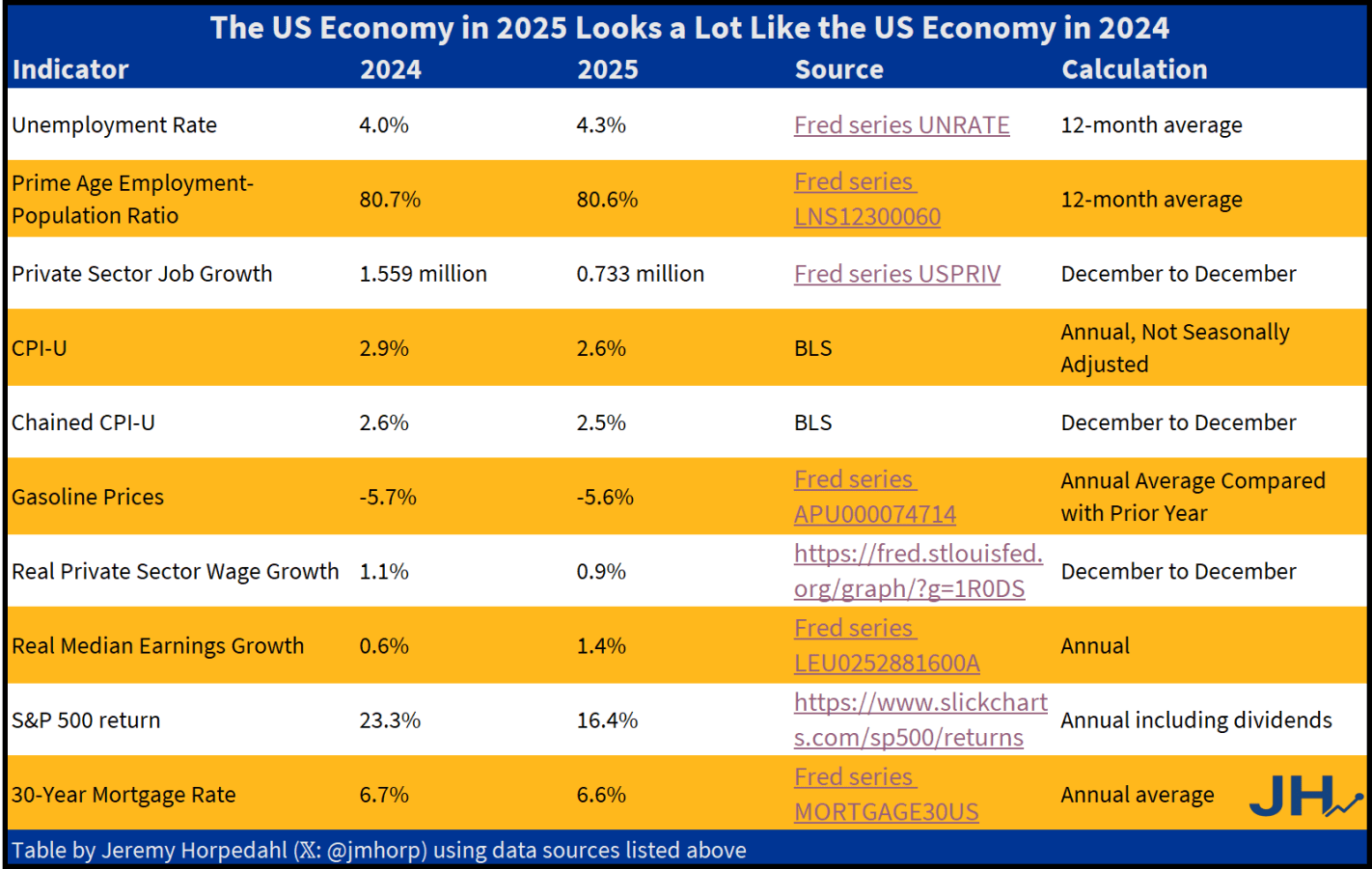
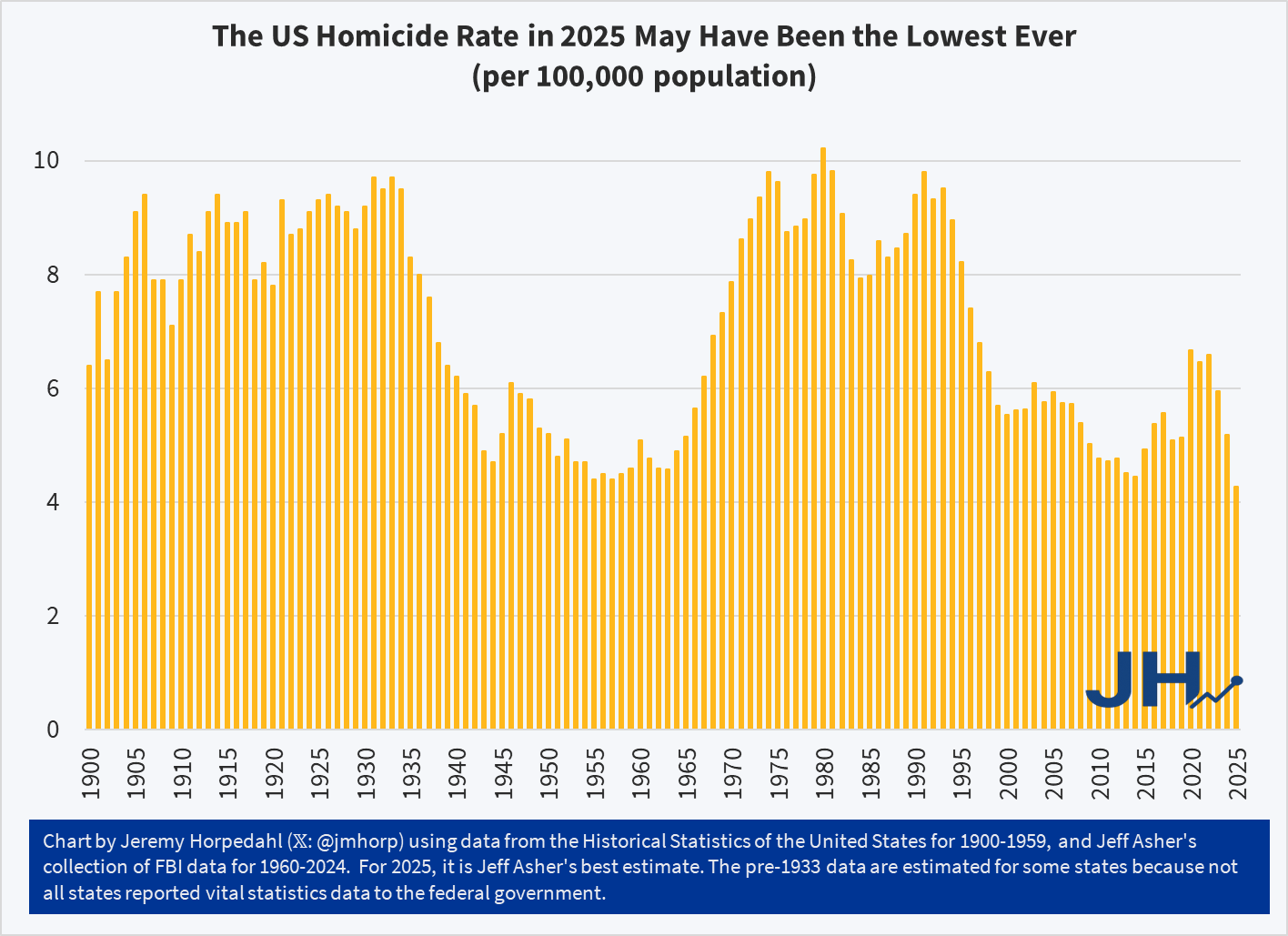
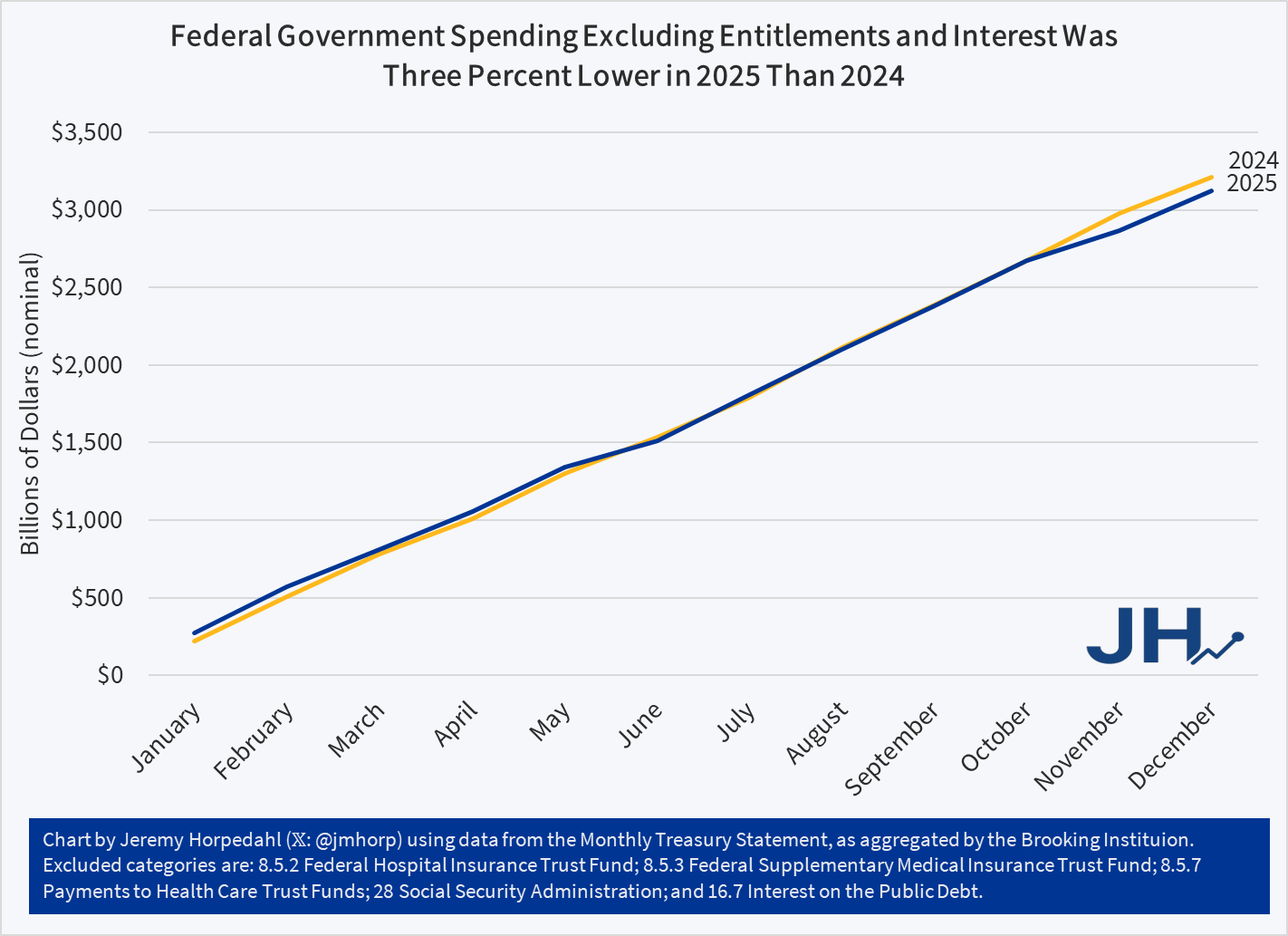
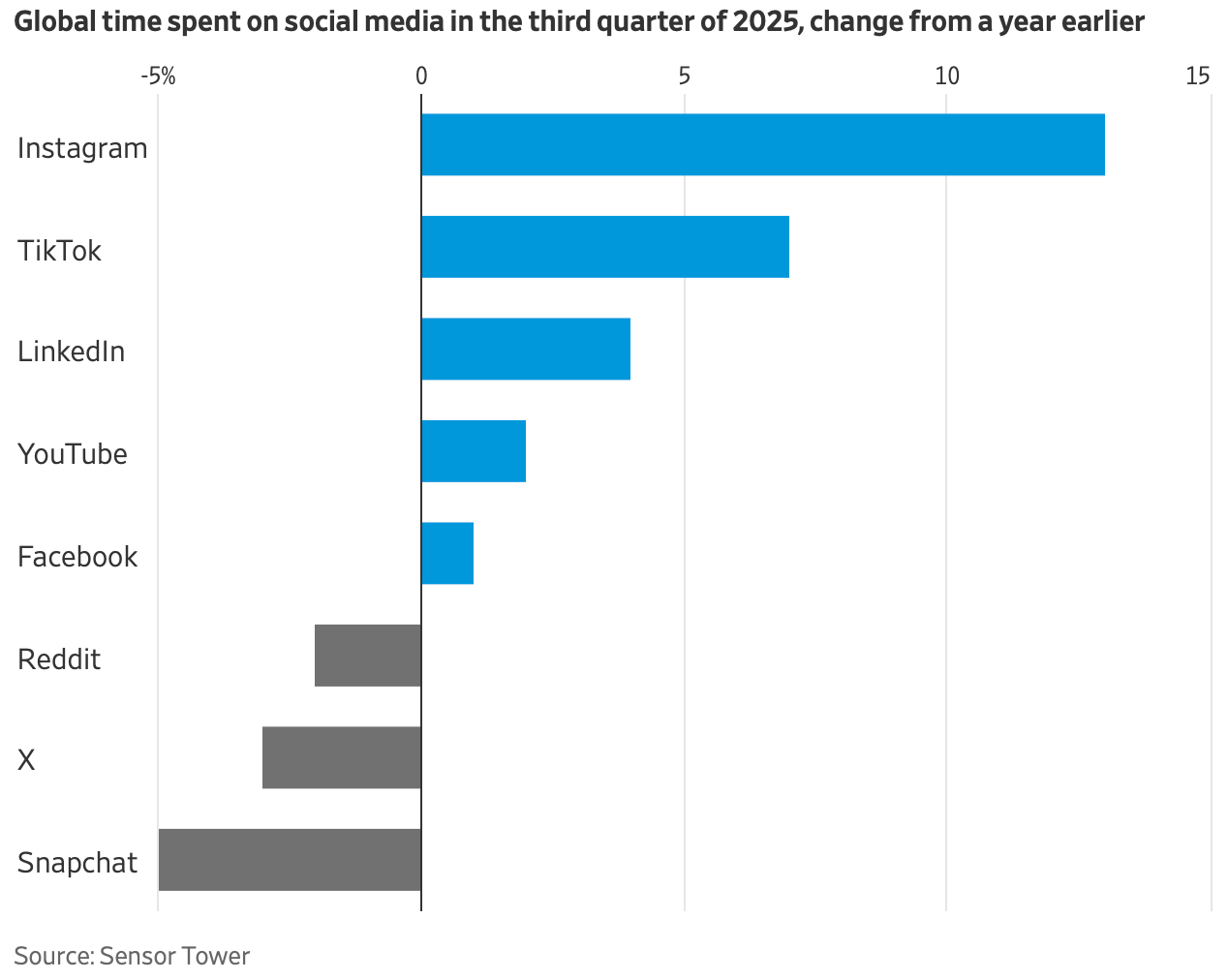The flu and covid-19 vaccines don’t work super well. Both vaccines permit infection and transmission at quite high rates. The benefit from these vaccines come largely from reductions in mortality or severe symptoms conditional on infection. The covid-19 vaccine is itself especially risky or ineffective depending on the age and health of the individual. Plenty of people eschew vaccines.
I live in Collier County, Florida where there have been 61 confirmed cases of measles so far this year. I have since learned that Measles is EXTREMELY contagious. It floats around the air and on items and just sort of hangs out and waits for a place to replicate. I’ve also learned that symptoms include a fever, eye irritation, possible brain swelling, severe dehydration, and a characteristic rash. The severe dehydration easily puts people in the hospital, the eye irritation can lead to permanent vision loss, and the brain swelling can be acute, or a symptom delayed by 5-6 years, which can also be fatal. I’ve also learned that having the vaccine, which is usually administered in two doses, provides about 97% immunity. The vaccine works so well, that the department of health recommends no behavioral change among the vaccinated population when there is a measles outbreak. Barring unique circumstances, measles immunity can persist for a lifetime.
Unfortunately, a large segment of the anti-vaccine mood affiliation retains the salience of the covid-19 vaccine characteristics. Other vaccines and diseases in the typical pediatric schedule are not similar. Most of these prevent infection >90% of the time (TDAP is low at 73%), prevent transmission, reduce mortality when there are breakthrough infections, are effective for years or decades, and are extremely safe for all age groups.
The risks of disease versus the corresponding vaccine are orders of magnitude away from each other. The tables below summarize the data (with sources). I did not double check the source on every single figure. If you glance below, then you’ll see why: Even if the numbers are closer by 10 or 100 times, vaccines still look really good.
First, mortality: The data is divided by disease and age group, and provides mortality rates for both the disease and for the vaccine. The numbers are proportions, conditional on infection or vaccination. There are a lot of zeros in the vaccine mortality rates and certainly more than for the diseases. For example, a measles infection is 10,000 more lethal than the MMR vaccine which prevents it. In fact, all of those zeros in the vaccine rates reflect mortality that is so uncommon, that the estimated one out of every 10 million is just rounded up because researchers don’t think that the risk is zero.
Continue reading